Applies to:
Finding LDAP (Lightweight Access Directory Protocol) settings
If you have access to Microsoft's Active Directory Domain Services Tool (part of Microsoft's Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) located under Server manager, you can use it to find LDAP information about your environment.
The AD Domain Services Tool stores directory data and manages communication between users and domains, including user logon processes, authentication, and directory searches. It is available on all windows servers.
If you need to install Microsoft's Remote Server Administration Tools, see Microsoft Technet article Installing Remote Server Administration Tools.
Identifying your LDAP settings using the AD Domain Services Tool:
- Click Start >Administrative Tools, and then open Active Directory Administrative Center.
Shortcut: Click Start, click Run, type dsac.exe, and then press Enter.
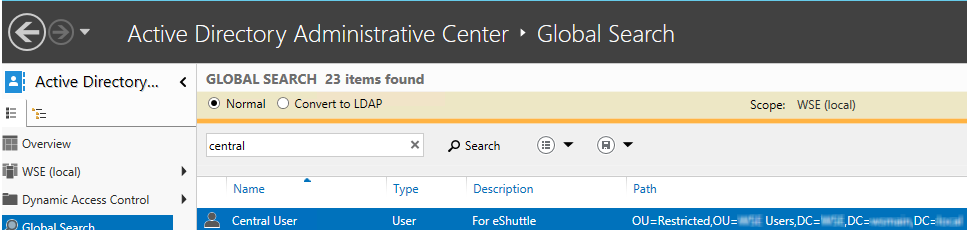
- On the Overview page, under Global Search, in the search field type the LDAP username and then click Search. (Note: This is the same username stored in the LMS Site settings under LDAP settings.)

- Select the value of the Path as shown in the example below. You only need the Domain component (DC) value from the path. For example: "DC=Contoso, DC=main, DC=Local".
- Open the LMS site.
- Click Settings.
- Click Site.
- Under LDAP Settings, click Edit, and then enter the LDAP information. See below for an example.
- Server Name: Hostname of the server. Example: MyServerName-1
- Username: The username used to connect to the LDAP site.
Note: You do not need to specify domain/username, only the username.
- Domain Name: The domain name. Example: MyCompanyDomain (First DC value from the left, i.e. top level DC)
- Organizational Unit: Provide remaining domain component value in following format: DC=<domain component>. Example: DC=Main, DC=Local.
Note: You do not need to specify Organizational Unit (OU), only the remaining Domain Component (DC).
Example: DC=Contoso, DC=Local